Galileo, Europe’s Global Navigation Satellite System
Galileo is Europe’s Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), providing improved positioning and timing information to many services and end-users. Galileo offers greater precision and accuracy to users, as well as improving the lives of European citizens through improved navigation, emergency response, more efficient roads and rails, and the creation of new products, services, and jobs.
The Galileo programme is funded and owned by the European Union and is thus under civilian control offering its data for free and for a broad range of applications. The programme is designed to be compatible and interoperable with all existing and planned GNSS providing a more seamless and accurate experience for multi-constellation users around the world.
System Architecture
Once fully deployed, the constellation will consist of 24 operational satellites with 6 in-orbit spares positioned in three orbital planes approximately 23 thousand kilometres above the Earth. These satellites use high-performance onboard clocks to deliver unparalleled performance and are complemented by an extensive network of ground sensor stations to relay information to and from the satellites, with the system being controlled by ground stations in Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany and Fucino, Italy.
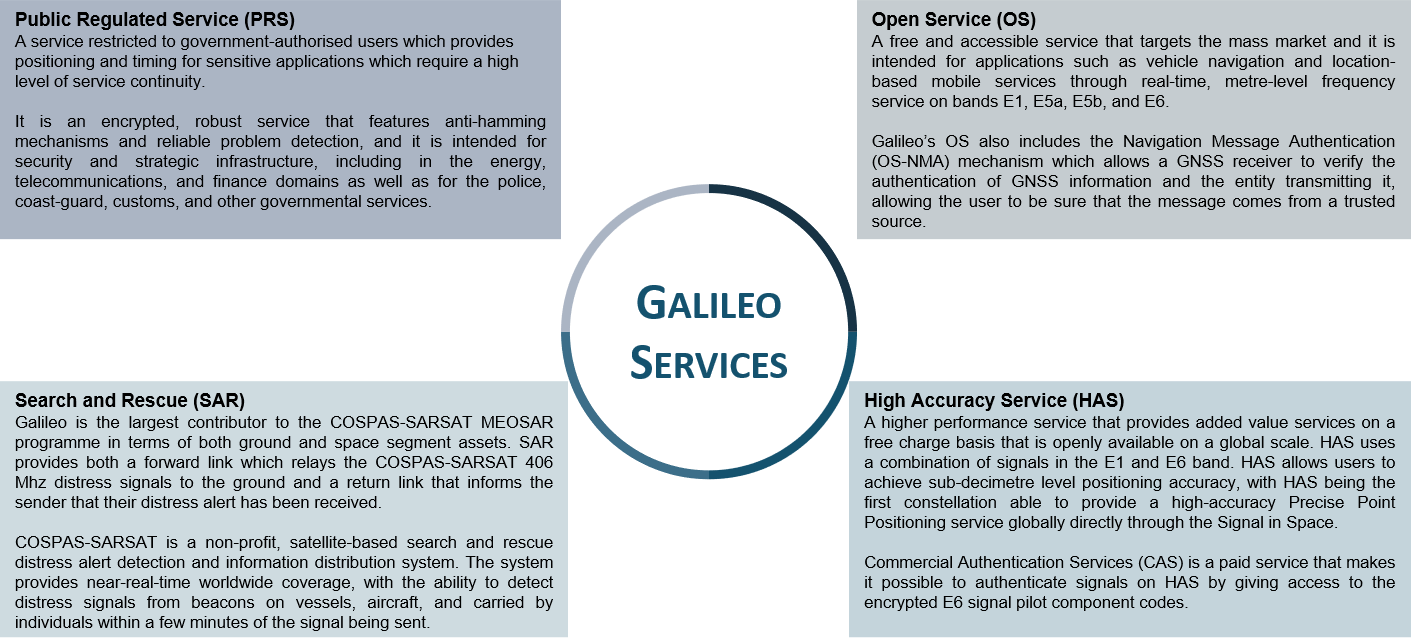
Once fully operational, Galileo will offer four high-performance core services worldwide:
Who is responsible?
The European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is responsible for Galileo and the user-oriented operational Agency of the EU Space Programme, contributing to sustainable growth, security and safety of the European Union. By fostering the development of innovative and competitive upstream and downstream sectors and engaging with the entire EU Space community worldwide, EUSPA is driving innovation-based economic growth.
EUSPA‘s goals related to Galileo & EGNOS are to:
- Provide long-term, state-of-the-art safe and secure Galileo and EGNOS positioning, navigation and timing services and cost-effective satellite communications services for GOVSATCOM, whilst ensuring service continuity and robustness;
- Communicate, promote, and develop the market for data, information and services offered by Galileo, EGNOS, Copernicus and GOVSATCOM;
- Contribute to maximising the socio-economic benefits of the EU Space Programme by fostering the development of a competitive and innovative downstream industry for Galileo, EGNOS, and Copernicus, leveraging also Horizon Europe, other EU funding mechanisms and innovative procurement mechanisms;
- Contribute to fostering the development of a wider European space ecosystem, with a particular focus on innovation, entrepreneurship and start-ups, and reinforcing know-how in Member States and Union regions.
Why Galileo?
According to the European Commission, 11% of the EU’s GDP is reliant on satellite navigation signals, a figure which showcases the importance of EGNSS to businesses in Europe and around the world.
This reliant on satellite location data means that Galileo is of strategic importance to these businesses due to its many advantages compared to the alternatives. The first of these advantages is that it is was built from the ground up to be an independent European system under civilian control, a direct contrast to the American GPS which is operated by the US Department of Defense which historically introduced errors into the civilian signals through selective availability.
Another key advantage of Galileo is that it has several signal frequencies that do not overlap with other GNSS’, meaning that attempts to jam or spoof GPS, BDS, or GLONASS will not impact the signal from Galileo. Finally, Galileo offers many other benefits such as a more reliable signal in urban environments, better positioning services at higher latitudes, and it is fully compatible for use in multi-constellation applications providing a more reliable and accurate service when compared to traditional single constellation applications.
Galileo Application Areas
Satellite-based navigation is a key enabler of a modern economy with GNSS signals being critical for many downstream market segments. Almost every downstream market can benefit in some way from the positioning and timing data from Galileo with EUSPA focusing on 10 specific downstream markets; consumer solutions, road & automotive, manned aviation, drones, maritime, emergency response, rail, agriculture, geomatics, and critical infrastructures.
There are countless examples of the benefits of Galileo for each of these markets, but, perhaps the most noticeable for the average person is the increasing application of Galileo in self-driving cars since 2019, an application that will greatly benefit from the greater accuracy that Galileo offers.
Aside from driverless cars, another key market that directly benefits from Galileo’s improved performance is the Search and Rescue (SAR) market. Galileo is the largest contributor to COSPAS-SARSAT, an international search and rescue initiative, reducing the time taken to locate emergency distress beacons from four hours to ten minutes.
Aside from these widely publicised benefits, Galileo’s performance enables innovation in the rail industry through fleet management and predictive maintenance, in the agriculture industry for soil condition monitoring and automatic steering of farm equipment, and even in critical infrastructure such as stock exchanges where Galileo is used to apply time stamps to executed trades.
To find out more about Galileo’s applications in downstream markets read the latest EUSPA GNSS Market Report that acts as a comprehensive source of knowledge and information on the global GNSS market.
In addition to the market report, EUSPA also provides a user technology report that takes an in-depth look at the latest state-of-the-art GNSS receiver technology, along with providing an expert analysis on the upcoming trends in the global GNSS landscape in the coming years.
EGNOS – SBAS in Europe
For situations where safety is critical, the European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS) provides a regional augmentation for global navigation satellite systems including Galileo. EGNOS operates over Europe and provides an integrity message for safety-of-life applications, allowing users to determine the correctness of the navigation signals they are receiving.
Consisting of three geostationary satellites and a network of over forty ground stations, EGNOS achieves its aim by measuring the performance of received GNSS signals over Europe and transmitting an augmentation signal to this. All measured GNSS errors are transferred to a central computing centre, where differential corrections and integrity messages are calculated. These calculations are then broadcast over the covered area using geostationary satellites that serve as an augmentation, or overlay, to the original GNSS message.
As a result, EGNOS improves the accuracy and reliability of GNSS positioning information, while also providing a crucial integrity message regarding the continuity and availability of a signal. In addition, EGNOS also transmits an extremely accurate universal time signal.
EGNSS in a multi-GNSS environment
European GNSS (EGNSS) does not exist in an isolated environment. For many users, particularly those in the multi-GNSS hotspots of Asia-Pacific, much of the value of EGNSS will be in using it in combination with other systems. Here, Galileo can be used in combination with global systems such as GPS, GLONASS, and BeiDou, and regional systems such as QZSS and IRNSS, to provide improved location information availability.
Galileo was designed to be interoperable with other systems such as GPS, and as such can offer easy integration into multi-GNSS solutions. With an increased number of potentially visible satellites, the availability of navigation information can be improved dramatically. This is particularly important in the large megacities of Asia-Pacific, where the presence of high-rise buildings can limit the visibility of individual GNSS constellations.
For more information on multi GNSS in the Asia and Oceania regions, visit the Multi-GNSS Asia website here.
GNSS.asia organises EGNSS training in Asia-Pacific. If you are interested, send a message to hello@gnss.asia